Design and Development
Before designing Malariaway, we first had to set out our design criteria. We focused on 4 factors (parentheses signifying ideal result):
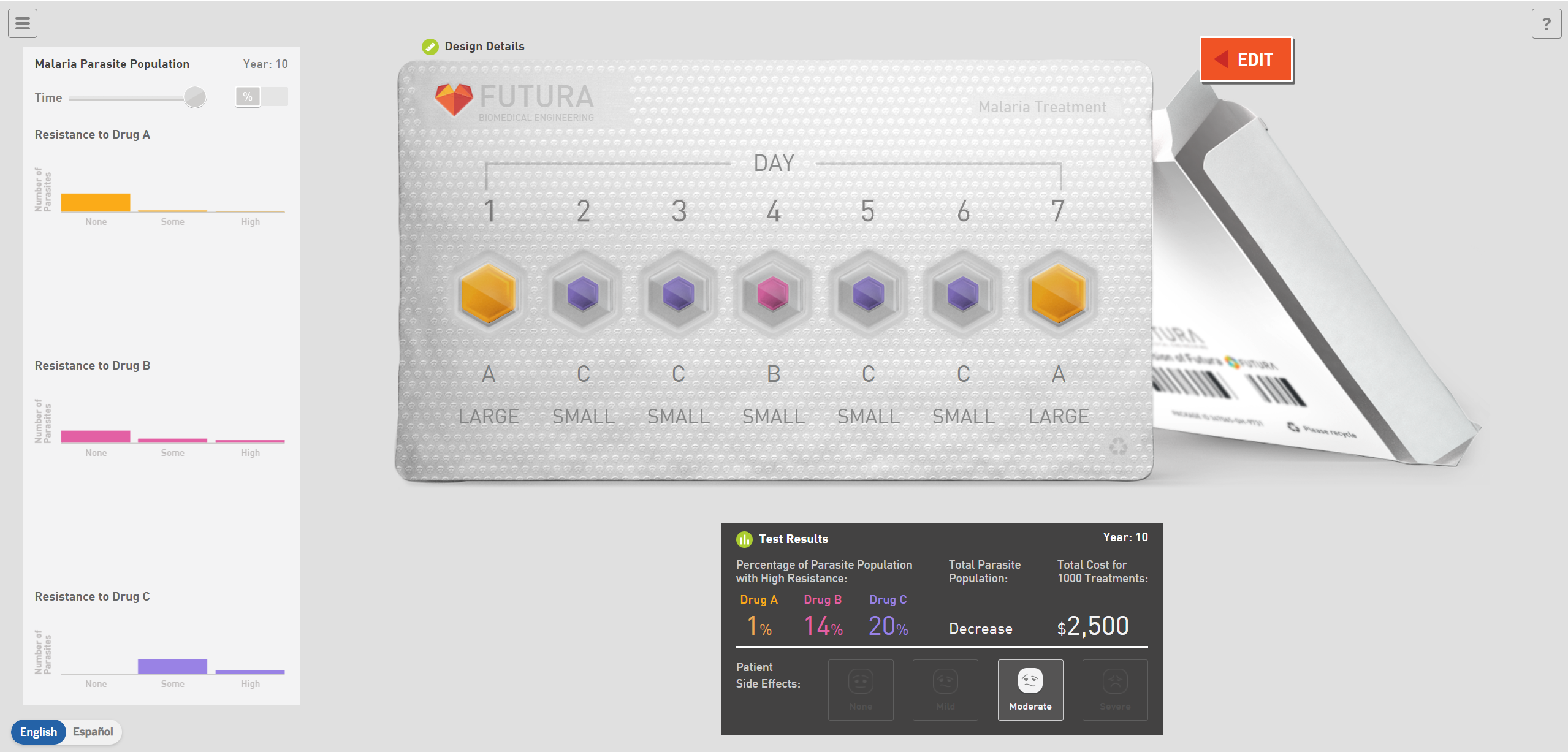
Copyright © 2024 Amplify Education Inc.
We chose to use a combination of three drugs, to improve effectiveness. The drug regimen is pictured above - the patient takes a large dose of drug A on days one and seven, a small dose of drug c on days two, three, five, and six, and a small dose of drug b on day 4. Our design costs $2,500 for 100 and results in moderate side effects. The TPP change over 10 years is a decrease, and drug resistance percentages below 20% for all three drugs.
As mentioned above, malaria parasites develop resistance to antimalarial drugs over time, due to natural selection. Drug resistance is not unique to malaria - other parasites, viruses, and bacterias also develop drug resistance. This is due to a mechanism known as natural selection. Initially, antimalarial drugs kill most of the malaria parasites. However, some parasites may possess genetic mutations that allow them to resist these drugs. The mutated parasites will then reproduce, and their offspring will also have drug-resistant genes. Over time, the population of the mutated parasites will grow, and the population of the parasites without the mutation will decrease as they are killed off. This causes the drug to be less effective, which necessitates the developement of new drugs which can kill the mutated strains.
We chose to prioritize two criteria: TPP change and parasite drug resistance. This was due to a number of factors. Firstly, we wanted to especially prioritize TPP change, so that the medicine would actually be effective in curing malaria. We chose to prioritize parasite drug resistance because it was the most feasible criteria to meet - we were unable to achieve mild or better side effects without costs and drug resistance ballooning, and were unable to achieve a cost under $2000 without incurring severe side effects and high drug resistance. Prioritizing drug resistance gave us acceptable results for cost and side effects, so we chose to prioritize it.
Return to Homepage